Ideal and Non-ideal Solutions
Ideal and Non-ideal Solutions: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Azeotropic Mixtures, Ideal Solution, Ideal and Non-ideal solutions, Non-Ideal Solutions, Fractional Distillation of Ideal Solution, Fractional Distillation of Non-Ideal Solutions and, Maximum Boiling Point Azeotropes
Important Questions on Ideal and Non-ideal Solutions
An ideal solution is formed by mixing two liquids. Which of the following options is CORRECT about change in enthalpy and change in volume upon mixing?
Use the phase diagram below to explain how you can obtain a pure sample of from a mixture by successively boiling and condensing the ideal liquid mixture.
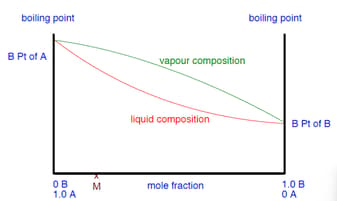
Fractional distillations can not separate an ideal mixture.
Nan-ideal solutions are separated by fractional distillation. What are negatively deviated non-ideal solutions? Give examples.
How does the non-ideal solutions separated?
The minimum boiling azeotrope have _____ from Raoult's law.
The negative deviation from Raoult's Law is observed when, the vapour pressure of the components is less than what is expected.
An ideal solution is that which
Write definition of azeotropic mixture _____
Separation of acetone and benzene from their mixture is carried out by
A mixture of of and of shows a positive deviation from ideality. A second mixture of of and of shows a negative deviation from ideality. Which of the following statements is true?
If liquid and forms an ideal solution, then the:-
On the basis of information given below mark the correct option.
Information : On adding acetone to methanol some of the hydrogen bonds between methanol molecules break.
If two liquids A and B form minimum boiling azeotrope at some specific composition then _____.
Considering the formation, breaking and strength of hydrogen bond, predict which of the following mixtures will show a positive deviation from Raoult’s law?
The property of an ideal solution is :
Which liquid pair solution show positive deviations?
Ethyl chloride mixed with ethyl bromide, which of the following is appropriate?
What is the total volume of the solution on mixing of acetone with of chloroform?
A mixture of two solvents and will show negative deviation in solution when
